Info
How do deep-water corals that do not have zooxanthellae feed?
According to the standardized literature, these corals feed by ingesting suspensions that are captured / held by polyps and later digested in the polyps' gastral cavity.
Some of the zooplankton may also be the so-called marine snow.
So far, so good!
The feeding habits of deep-sea octocorals have hardly been studied so far.
Over many years, here we single out the years 2011, 2021 and 2024, scientific papers with really interesting news about the nutrition of deep-water corals have been published.
The main prey items of deep-sea corals and anemones are gelatinous zooplankton, various echinoderms and planktonic tunicates, whereby the gelatinous zooplankton includes dead and also living jellyfish and salps such as Salpa thompsoni Foxton, 1961, so really large prey items!
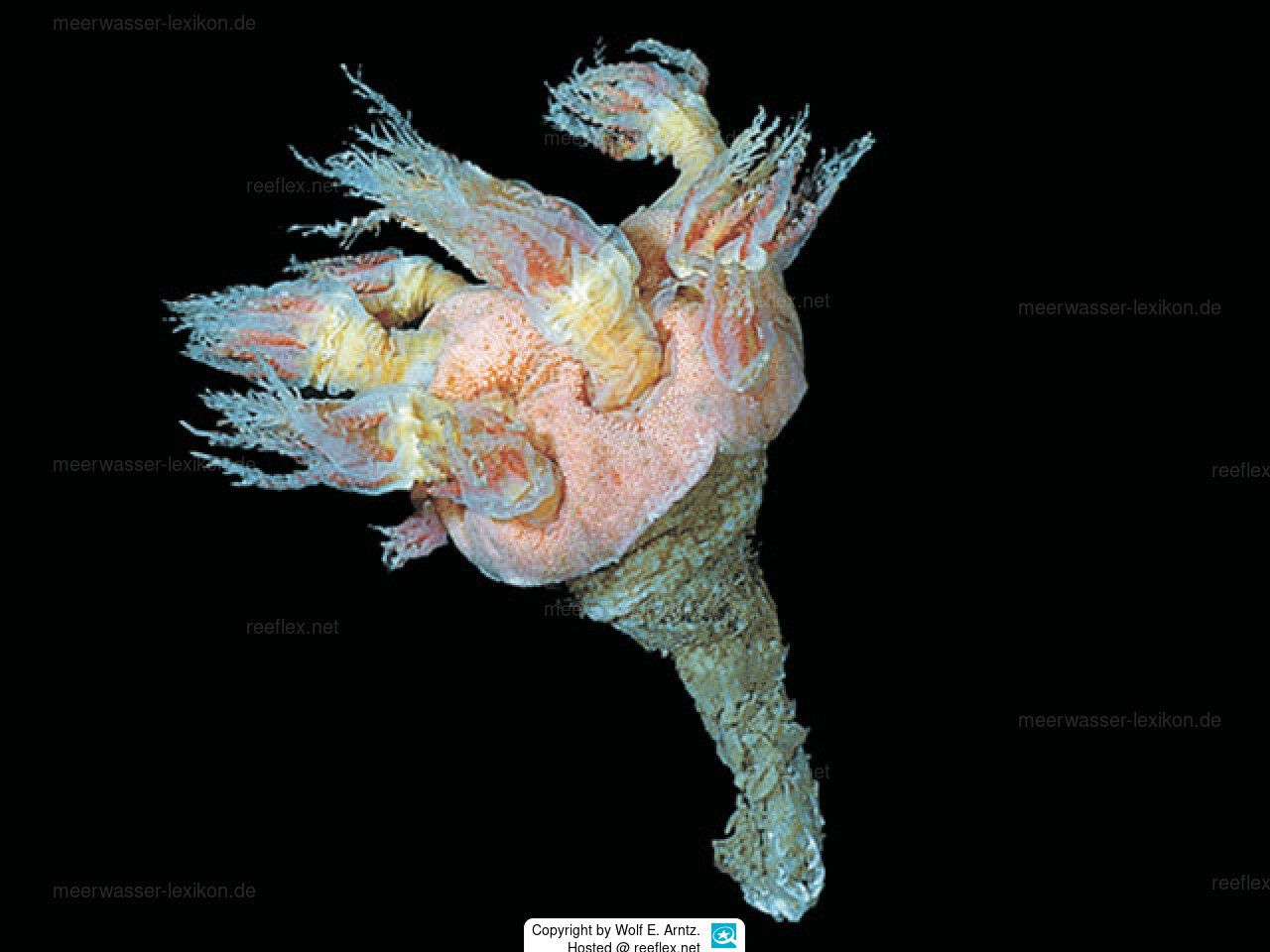
Orejas et al. (2002a) examined the contents of the gastrovascular cavity of polyps of the species Anthomastus bathyproctus, which were collected at a depth of over 400 meters off the Antarctic Peninsula.
All of the more than 100 polyps examined from eight colonies had remains of a salp, Salpa thompsoni, in their gut!
Due to the different sizes of predator and prey, the authors of the article “Big enough for an extra-large meal: a review on predation upon large animals by benthic cnidarians” recommend
the following new definitions
Micropredation (predator-to-prey size ratio ≥ 5:1)
and
macropredation (predator-to-prey size ratio ≤ 1:1)
We recommend that anyone interested in the subject studies the following reports, which we have provided under “Further links”:
- Big enough for an extra-large meal: a review on predation upon large animals by benthic cnidarians
- Chapter Two - Biology of Deep-Water Octocorals
- Salpivory by Colonial Reef Corals at Curaçao, Southern Caribbean
Synonym: Anthomastus (Anthomastus) bathyproctus Bayer, 1993
According to the standardized literature, these corals feed by ingesting suspensions that are captured / held by polyps and later digested in the polyps' gastral cavity.
Some of the zooplankton may also be the so-called marine snow.
So far, so good!
The feeding habits of deep-sea octocorals have hardly been studied so far.
Over many years, here we single out the years 2011, 2021 and 2024, scientific papers with really interesting news about the nutrition of deep-water corals have been published.
The main prey items of deep-sea corals and anemones are gelatinous zooplankton, various echinoderms and planktonic tunicates, whereby the gelatinous zooplankton includes dead and also living jellyfish and salps such as Salpa thompsoni Foxton, 1961, so really large prey items!
Orejas et al. (2002a) examined the contents of the gastrovascular cavity of polyps of the species Anthomastus bathyproctus, which were collected at a depth of over 400 meters off the Antarctic Peninsula.
All of the more than 100 polyps examined from eight colonies had remains of a salp, Salpa thompsoni, in their gut!
Due to the different sizes of predator and prey, the authors of the article “Big enough for an extra-large meal: a review on predation upon large animals by benthic cnidarians” recommend
the following new definitions
Micropredation (predator-to-prey size ratio ≥ 5:1)
and
macropredation (predator-to-prey size ratio ≤ 1:1)
We recommend that anyone interested in the subject studies the following reports, which we have provided under “Further links”:
- Big enough for an extra-large meal: a review on predation upon large animals by benthic cnidarians
- Chapter Two - Biology of Deep-Water Octocorals
- Salpivory by Colonial Reef Corals at Curaçao, Southern Caribbean
Synonym: Anthomastus (Anthomastus) bathyproctus Bayer, 1993






 Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Wolf E. Arntz, Deutschland
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Wolf E. Arntz, Deutschland

